Expert Causal Agent is an LLM-driven autonomous system that simplifies causal discovery and inference by automating the full analytical workflow. By integrating over twenty state-of-the-art causal methods, it enables reliable, scalable causal analysis beyond correlation, making rigorous causal reasoning accessible without deep statistical expertise.

Overview
Causal analysis is essential for moving beyond correlation to uncover the mechanisms that drive phenomena across science, medicine, economics, and engineering. Despite its theoretical maturity, causal discovery and inference remain notoriously difficult to apply in practice. Existing methods demand deep statistical expertise, involve complex algorithmic decision-making, and often fail to scale to real-world datasets.
Causal-Copilot addresses these limitations by introducing an LLM-driven autonomous agent that performs end-to-end causal analysis. The system integrates natural language reasoning, automated orchestration of causal algorithms, statistical validation, and interpretability within a unified framework. By incorporating more than twenty state-of-the-art causal methods, Causal-Copilot democratizes causal reasoning—making it accessible to non-experts while preserving methodological rigor.
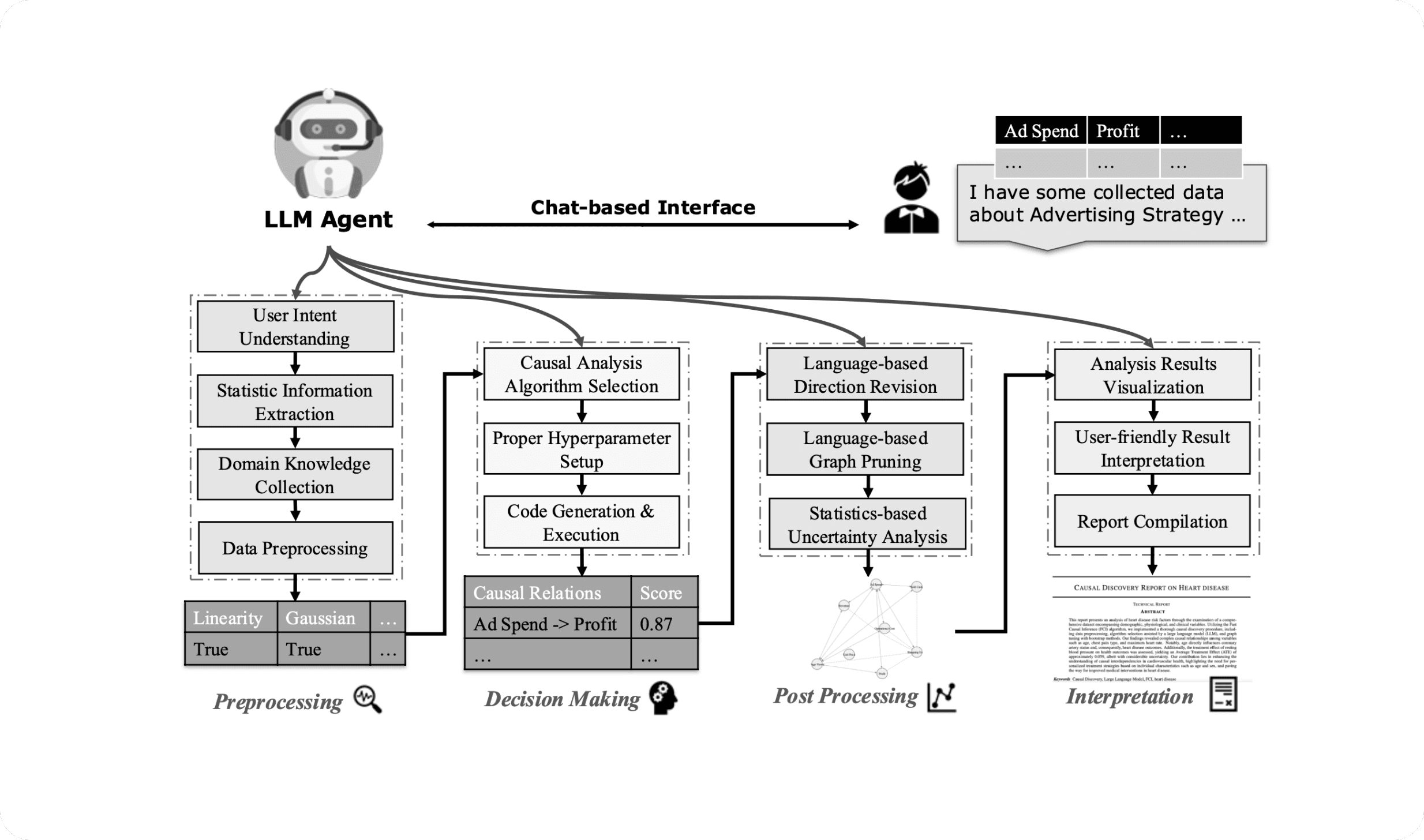
The overall workflow of our Causal-Copilot, with an example of discovering
the causal structure in collected advertising related data.
Motivation
Understanding cause–effect mechanisms is foundational to scientific discovery, clinical decision-making, economic policy, and engineering optimization. However, several obstacles hinder the widespread adoption of causal methods. These include the steep learning curve associated with causal discovery and inference, the diversity and complexity of available algorithms, and the lack of large-scale deployment and real-world validation.
As a result, a significant research gap persists: although causal methods are theoretically well-developed, they remain practically inaccessible to most practitioners. Causal-Copilot is designed to bridge this gap by lowering the barrier to entry while maintaining statistical soundness.
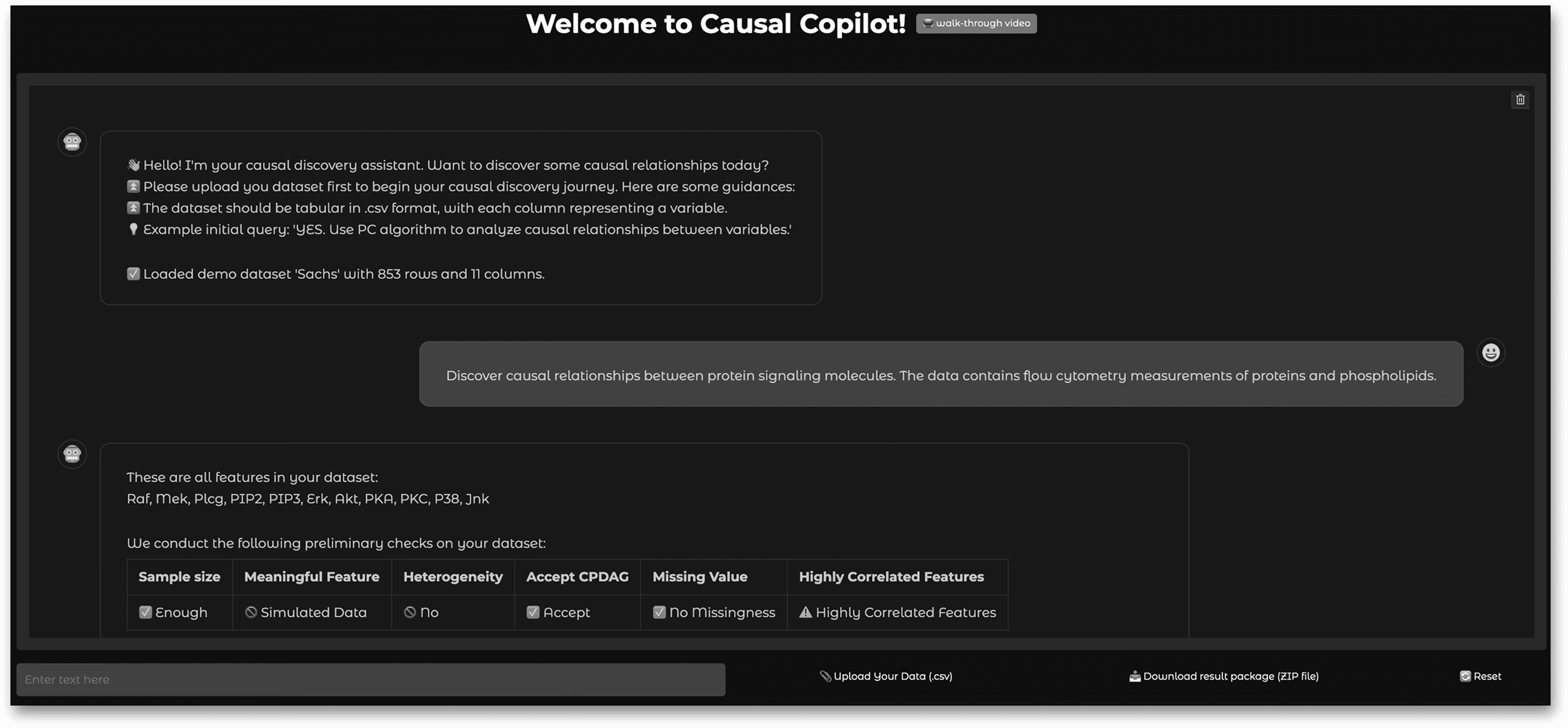
The website demo of our Causal-Copilot
System Design
Causal-Copilot adopts a modular architecture orchestrated by a large language model, enabling seamless transitions from raw data to actionable causal insights. Users interact with the system through natural language, eliminating the need for coding or specialized statistical tooling.
The preprocessing pipeline automatically performs data cleaning, schema extraction, and statistical diagnostics. An intelligent algorithm selection engine then filters and ranks candidate causal methods based on data characteristics and task requirements, configures hyperparameters, and executes the analysis workflow.
Postprocessing includes bootstrap-based confidence estimation and LLM-driven conceptual refinement, ensuring both statistical robustness and semantic validity. The system produces interpretable outputs such as causal graphs, effect estimates, counterfactual simulations, and structured PDF reports suitable for decision-making and communication.
Supported Methods
Causal-Copilot integrates a comprehensive library of causal techniques. For causal discovery, supported methods include PC, FCI, GES, FGES, NOTEARS, GOLEM, LiNGAM, PCMCI, and DYNOTEARS.
For causal inference, the system incorporates Double Machine Learning, Doubly Robust Estimation, Instrumental Variable methods, matching techniques such as Propensity Score Matching (PSM) and Coarsened Exact Matching (CEM), as well as counterfactual estimation approaches.
Auxiliary tools include SHAP-based feature importance analysis, anomaly detection, and root cause analysis. To support large-scale data, the system provides CPU parallelization and GPU acceleration.
Reference
Xinyue Wang, Kun Zhou, Wenyi Wu, Har Simrat Singh, Fang Nan, Songyao Jin, Aryan Philip, Saloni Patnaik, Hou Zhu, Shivam Singh, Parjanya Prashant, Qian Shen, Biwei Huang.
“Causal-Copilot: An Autonomous Causal Analysis Agent.”
arXiv preprint arXiv:2504.13263, 2025.
© 2026 Abel Intelligence Inc. All rights reserved
System
Platform
Trust
Legal
Community